Reinsurgence of Marburg virus disease (MVD) in Uganda
On 19 October 2017 the Ministry of Health of Uganda reported that a case of Marburg virus disease (MVD) has been confirmed on 17 October in the country by the Uganda Virus Research Institute (UVRI)1.
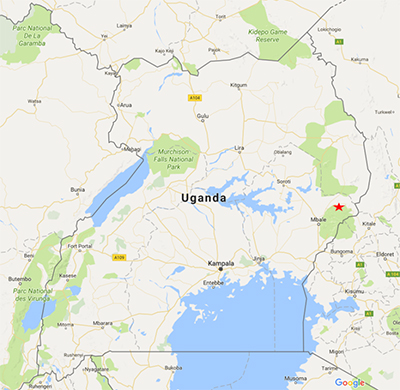
The confirmed case is a 50-year-old female from Chemuron village, Kween District on the western slopes of Mt Elgon in Eastern Uganda. She showed symptoms suggestive of a viral hemorrhagic fever (VHF) and died during the night of 11 Oct 2017 at Kapchorwa Hospital. Preliminary field investigations indicated that prior to her death the deceased had nursed her 42-year-old brother, who had died on 25 Sep 2017 with similar signs and symptoms. She had also closely participated in the cultural preparation of the body for burial. The brother was reported to be a hunter who carried out his activities where there are caves with heavy presence of bats. However, no samples were taken off his body prior to his death. The Ministry of Health is sending an emergency response team to the district.
Marburg virus disease (MVD) is caused by the Marburg virus, a rare but severe type of viral hemorrhagic fever which affects both humans and non-human primates like monkeys, baboons. The reservoir host of Marburg virus is the African fruit bat (Egyptian fruit bat, Rousettus aegyptiacus). Fruit bats infected with Marburg virus do not show signs of illness. Primates (including humans) are vulnerable to contracting the Marburg virus, which is known to have a very high mortality. MVD previously occurred in Uganda in 2014 (1 confirmed case, 1 death) and in 2012 (15 cases, 4 deaths). More information on MVD can be found at dedicated web page of World Health Organization (WHO)2.
__________________ 1 http://www.mediacentre.go.ug/press-release/press-statement-marburg-virus-disease
© IZSAM October 2017
|
|
Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale
dell'Abruzzo e del Molise "G. Caporale"
Campo Boario | 64100 TERAMO | ITALIA
Telefono 0039.0861.3321 | Fax 0039.0861.332251
e-mail: archivioeprotocollo@izs.it
Posta elettronica certificata: protocollo@pec.izs.it
Partita IVA: 00060330677
Codice Fiscale: 80006470670